Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sm by ICP-MS/MS
Sm by ICP-MS/MSHorita, Takuma; Akimoto, Yuji*; Do, V. K.
no journal, ,
Samarium-151( Sm) can be measured by liquid scintillation counting (LSC) or inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). While the former method requires a complete radiochemical separation, the latter one must solve the isobaric interference from Europium-151 (
Sm) can be measured by liquid scintillation counting (LSC) or inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). While the former method requires a complete radiochemical separation, the latter one must solve the isobaric interference from Europium-151 ( Eu). In this study, we have been developing an analytical technique for
Eu). In this study, we have been developing an analytical technique for  Sm by ICP-tandem MS(ICP-MS/MS). The recent advances of MS/MS mode with a collision/reaction cell in mass spectrometry may enable sufficient removal of the mass spectroscopic interferences. Moreover, compared to LSC, ICP-MS is more rapid and more selective, and thus, it can simplify pretreatment process. As preliminary experiments, the selection of reaction gas for the separation of
Sm by ICP-tandem MS(ICP-MS/MS). The recent advances of MS/MS mode with a collision/reaction cell in mass spectrometry may enable sufficient removal of the mass spectroscopic interferences. Moreover, compared to LSC, ICP-MS is more rapid and more selective, and thus, it can simplify pretreatment process. As preliminary experiments, the selection of reaction gas for the separation of  Sm from
Sm from  Eu were examined by checking the product ions of
Eu were examined by checking the product ions of 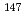 Sm and
Sm and  Eu produced by reactions with the various gases (H
Eu produced by reactions with the various gases (H , O
, O , NH
, NH , and N
, and N O). Our obtained data showed that in the reaction with NH
O). Our obtained data showed that in the reaction with NH , Sm formed a product ion at mass shift of 16, while the reaction tendency of Eu is different. Accordingly, the counts of
, Sm formed a product ion at mass shift of 16, while the reaction tendency of Eu is different. Accordingly, the counts of 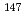 Sm and
Sm and  Eu at the mass shift of 16 were 9842 [cps/
Eu at the mass shift of 16 were 9842 [cps/ g/L] and 162 [cps/
g/L] and 162 [cps/ g/L], respectively. The difference in reactivity of Sm and Eu to NH
g/L], respectively. The difference in reactivity of Sm and Eu to NH gas can reduce interference of the
gas can reduce interference of the  Eu to the measurement of
Eu to the measurement of  Sm.
Sm.
Toh, Yosuke; Maeda, Makoto; Tsuneyama, Masayuki*; Segawa, Mariko; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 I/
I/ I ratio in underground water by accelerator mass spectrometry at Tono Geoscience Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency
I ratio in underground water by accelerator mass spectrometry at Tono Geoscience Center, Japan Atomic Energy AgencyFujita, Natsuko; Okabe, Nobuaki*; Matsubara, Akihiro; Miyake, Masayasu*; Kokubu, Yoko; Watanabe, Takahiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Ra activity; A Case study of the groundwater from the former uranium open pit mine at Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center of JAEA
Ra activity; A Case study of the groundwater from the former uranium open pit mine at Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center of JAEATomita, Jumpei; Takeuchi, Erina; Ohara, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Koarai, Kazuma; Matsueda, Makoto; Fujiwara, Kenso; Ono, Takumi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Oka, Toshitaka; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have investigated incorporation of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs in teeth of cattle and otoliths of fish. Specific activity of
Cs in teeth of cattle and otoliths of fish. Specific activity of  Sr in the dentin tissue was higher than that in the enamel tissue. The result shows change of
Sr in the dentin tissue was higher than that in the enamel tissue. The result shows change of  Sr incorporation in cattle even within a tooth. Concentrations of stable Sr and Cs were 94 ppm and 3 ppb. Distributions of stable Sr and Cs were uniform in the otolith of fish. If distribution of
Sr incorporation in cattle even within a tooth. Concentrations of stable Sr and Cs were 94 ppm and 3 ppb. Distributions of stable Sr and Cs were uniform in the otolith of fish. If distribution of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs in the otolith was measured, change of
Cs in the otolith was measured, change of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs incorporation into the fish would be found. These findings suggest that distribution patterns of
Cs incorporation into the fish would be found. These findings suggest that distribution patterns of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs in the environment could be estimated from distribution of the radionuclides in the tooth and otolith.
Cs in the environment could be estimated from distribution of the radionuclides in the tooth and otolith.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Kobayashi, Toru; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
In this study, we investigated the deposits formed in the electrolytic deposition of U in pH2 3 solutions by absorption spectroscopy and X-ray Absorption Fine Structure (XAFS). The absorption spectrum of U(V) just after electrolysis was measured. The baseline rise with the light scattering of U deposits and the absorption with U(IV) were observed. The increase of deposition and the absorption of U(VI) were observed with time. These results showed that U(IV) and U(VI) were formed by the disproportionation of U(V), and U(IV) formed deposits. The XAFS spectrum of electrolytic deposits formed in pH 2 was measured. The species of the deposits was identified as U(IV) hydroxide. It was found that the electrolytic deposition in pH2
3 solutions by absorption spectroscopy and X-ray Absorption Fine Structure (XAFS). The absorption spectrum of U(V) just after electrolysis was measured. The baseline rise with the light scattering of U deposits and the absorption with U(IV) were observed. The increase of deposition and the absorption of U(VI) were observed with time. These results showed that U(IV) and U(VI) were formed by the disproportionation of U(V), and U(IV) formed deposits. The XAFS spectrum of electrolytic deposits formed in pH 2 was measured. The species of the deposits was identified as U(IV) hydroxide. It was found that the electrolytic deposition in pH2 3 is different from the deposition in pH 4 which changes to oxide as a terminal product.
3 is different from the deposition in pH 4 which changes to oxide as a terminal product.
Matsueda, Makoto; Koarai, Kazuma; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kitamura, Akihiro
no journal, ,
Radionuclide analysis of environmental water requires large amount of samples to be concentrated, because generally the radionuclide level is very low. In order to achieve rapid and simple concentration method, we applied homogeneous liquid-liquid extraction for sample enrichment. This method extracts the desired solute existing in the homogeneous solution into the water-immiscible phase by time and pH dependent phase separations. Since the method forms large surface area of the interface between the solvent and the desired solute, we only need small amount of extraction solvents to migrate desired solute into the formed phase. In this study, we tried two kind of phase separation phenomenon. (1) pH dependent extraction. (2) Ionic liquid extraction.
Satou, Yukihiko; Sueki, Keisuke*; Ishii, Tatsuya*; Igarashi, Junya*; Martin, P.*; Jones, C.*; Scott, T.*
no journal, ,
In Fukushima accident, insoluble radioactive Cs particles found at the northwestern region from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station (1FNPS). Presence of Cs particle in other surrounding area from 1FNPS is unclear yet. In the present study, the presence of other particle emission events and the presence of new types of radioactive particles were investigated by expanding the search object to soil samples collected outside the 1FNPS northwest region where insoluble Cs particles were reported. Four radioactive particles found from the samples. The particles look like pebbles and diameter is 0.4 to 2 mm, and the size feature is Type B. Isotopic ratio of Cs is very similar to type A of 1.0. EDS results confirmed the presence of iron and aluminum in addition to silicon. Further, in the CT image, there was an absorption point near the surface indicating that the element is heavier than iron. Although these features are clearly different from the insoluble Cs particles that have been reported in the past, in this implementation item it is not possible to find the location where Cs is adsorbed, and further direct emission from uranium or in the reactor.
Tomita, Ryohei; Esaka, Fumitaka; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Suzuki, Daisuke; Miyamoto, Yutaka
no journal, ,
The research group for safeguards analytical chemistry which belong to Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) introduced new Large Geometry Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (LG-SIMS) instrument (1300-HR , CAMECA) to update our capability. LG-SIMS instrument has higher mass resolving power (MRP) than small geometry SIMS (SG-SIMS) instrument we had used. We hope molecular interferences (e.g. Pb, Al, Fe) are removed by LG-SIMS instrument when we analyze uranium bearing particles in environmental sample. In order to obtain the bes LG-SIMS condition for uranium particle analysis, we investigated a relationship between MRP, secondary ion's intensity and peak shape of uranium. One of the most famous molecular interferences of uranium SIMS analysis is PbAl
, CAMECA) to update our capability. LG-SIMS instrument has higher mass resolving power (MRP) than small geometry SIMS (SG-SIMS) instrument we had used. We hope molecular interferences (e.g. Pb, Al, Fe) are removed by LG-SIMS instrument when we analyze uranium bearing particles in environmental sample. In order to obtain the bes LG-SIMS condition for uranium particle analysis, we investigated a relationship between MRP, secondary ion's intensity and peak shape of uranium. One of the most famous molecular interferences of uranium SIMS analysis is PbAl (mass number: 234, 235). If we attempt to remove molecular interferences of the PbAl
(mass number: 234, 235). If we attempt to remove molecular interferences of the PbAl from uranium mass regions, MRP value of 2741 is required. The MRP of LG-SIMS instrument is defined by entrance and exit slit. We need to keep balance between MRP, secondary ion's intensity and flat-top peak rate. We compared some combination of entrance and exit slit to get better balance. We found the best combination of entrance and exit slit is sized 200
from uranium mass regions, MRP value of 2741 is required. The MRP of LG-SIMS instrument is defined by entrance and exit slit. We need to keep balance between MRP, secondary ion's intensity and flat-top peak rate. We compared some combination of entrance and exit slit to get better balance. We found the best combination of entrance and exit slit is sized 200  m and 500
m and 500  m, respectively. LG-SIMS can almost remove PbAl
m, respectively. LG-SIMS can almost remove PbAl from uranium secondary ions in this condition. This research is part of investigation into safeguards analysis techniques commissioned by nuclear regulatory agency.
from uranium secondary ions in this condition. This research is part of investigation into safeguards analysis techniques commissioned by nuclear regulatory agency.
 with
with  -Raman spectroscopy and X-ray absorption spectroscopy
-Raman spectroscopy and X-ray absorption spectroscopyYomogida, Takumi; Ouchi, Kazuki; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Kobayashi, Toru; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
A combination of micro-Raman spectroscopy (MRS), and X-ray absorption spectroscopy was applied to the characterization of uranium dioxide (UO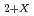 ). A fresh UO
). A fresh UO immediately after preparation, an aged UO
immediately after preparation, an aged UO after 30 years storage were employed. In X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectra, the absorption edge of the aged UO
after 30 years storage were employed. In X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectra, the absorption edge of the aged UO sample was shifted to higher energy. This result indicates that the aged UO
sample was shifted to higher energy. This result indicates that the aged UO was slightly oxidized. Characteristic Raman bands at 447, and 1150 cm
was slightly oxidized. Characteristic Raman bands at 447, and 1150 cm which derived from UO
which derived from UO structure were observed in both the flesh and the aged UO
structure were observed in both the flesh and the aged UO . The ratio of a Raman peak at 1150 cm
. The ratio of a Raman peak at 1150 cm to at 447 cm
to at 447 cm of the fresh UO
of the fresh UO is higher than that of the aged UO
is higher than that of the aged UO . These results are showing the applicability of the proposed methods to analyzing the oxidation of UO
. These results are showing the applicability of the proposed methods to analyzing the oxidation of UO .
.
 Cs/
Cs/ Cs ratio in indoor dust from near the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant
Cs ratio in indoor dust from near the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power PlantMinowa, Haruka*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Nakama, Shigeo; Satou, Yukihiko; Sueki, Keisuke*
no journal, ,
In this study, we aimed to estimate the diffusion distribution of radioactive Cs from each reactor source using the environmental samples. First, the influence of the sum-peak effect on the counting efficiency of  Cs in the Ge detector was investigated for the accurately radioactive measurement, and applied it to the actual sample. To measure the variation of the counting efficiency depends on the distance between the Ge detector and a sample, a disk-shaped standard sample (25 mm
Cs in the Ge detector was investigated for the accurately radioactive measurement, and applied it to the actual sample. To measure the variation of the counting efficiency depends on the distance between the Ge detector and a sample, a disk-shaped standard sample (25 mm of filter paper) and a particle standard sample (200
of filter paper) and a particle standard sample (200  m in size) were used. When the sample was placed close to the detector (distance 0.1 mm), the counting efficiency [cps/Bq] of
m in size) were used. When the sample was placed close to the detector (distance 0.1 mm), the counting efficiency [cps/Bq] of  Cs was about 20% lower than that of
Cs was about 20% lower than that of  Cs in both the disk-shaped and the particle standard sample. It seemed to be caused by the sum-peak effect. "Smear paper" samples with indoor dust collected from about 40 points within 10 km from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in 2014-2019 were measured, and
Cs in both the disk-shaped and the particle standard sample. It seemed to be caused by the sum-peak effect. "Smear paper" samples with indoor dust collected from about 40 points within 10 km from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in 2014-2019 were measured, and  Cs and
Cs and  Cs were quantified using the counting efficiency with the disk-shaped standard sample. From the
Cs were quantified using the counting efficiency with the disk-shaped standard sample. From the  Cs/
Cs/ Cs ratio at the time of the accident, the mixing ratio of materials derived from Reactors 1, 2 and 3 was estimated, and the spatial diffusion distribution of radioactive materials for each reactor was indicated.
Cs ratio at the time of the accident, the mixing ratio of materials derived from Reactors 1, 2 and 3 was estimated, and the spatial diffusion distribution of radioactive materials for each reactor was indicated.
Igarashi, Junya*; Zheng, J.*; Zhang, Z.*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Satou, Yukihiko; Fukuda, Miho*; Ni, Y.*; Aono, Tatsuo*; Shinohara, Atsushi*
no journal, ,
Plutonium is one of the most notable radionuclides in the nuclear accident. The amounts of Pu released by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident were investigated so far. However, the existence of Pu isotopes from the global fallout makes it difficult to accurately assessment of Pu contamination by the FDNPP accident. To avoid this problem, identification of Pu contamination source from the Pu isotopic ratios is important. However, various ratios have been reported by the researches due to the contamination from global fallout. In this work, we focused on the insoluble radioactive Cs particles made of mainly SiO (insoluble particles) released from the FDNPP to determine accurate Pu isotopic ratios. Due to its insolubility, the particles retained the original property at the time of emission from the reactor. Therefore, the insoluble particles are considered to be free from the contamination of global fallout. In addition, the amounts of Pu in the insoluble particles provide the information about their formation process in the reactor. In this study, we identified Pu isotopes in insoluble particles by radioactive analysis and ICP-MS measurement. The isotopic ratios of
(insoluble particles) released from the FDNPP to determine accurate Pu isotopic ratios. Due to its insolubility, the particles retained the original property at the time of emission from the reactor. Therefore, the insoluble particles are considered to be free from the contamination of global fallout. In addition, the amounts of Pu in the insoluble particles provide the information about their formation process in the reactor. In this study, we identified Pu isotopes in insoluble particles by radioactive analysis and ICP-MS measurement. The isotopic ratios of  Pu/
Pu/ Pu and
Pu and  Pu/
Pu/ Pu were determined as 0.330-0.415 and 0.162-0.178, respectively and activity ratio of
Pu were determined as 0.330-0.415 and 0.162-0.178, respectively and activity ratio of  Pu/
Pu/ Cs was about 10
Cs was about 10 in each particle.
in each particle.
Ishii, Tatsuya*; Sueki, Keisuke*; Matsuo, Kazuki*; Kurosawa, Masanori*; Satou, Yukihiko; Kobata, Masaaki; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Yoshii, Kenji; Tanida, Hajime; Okane, Tetsuo; et al.
no journal, ,
Radioactive particles were released into the environment by the accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP). They have information to understand the inside of the reactor during the accident. Now, nobody knows the generation process of radioactive particles. In this study, we analyzed (1) elements of particles' cross section with SEM-EDS to reveal what is the material and (2) chemical states of elements on particles' surface with HAXPES. (1) Radioactive particles are composed of the two parts. One is the basic material and the other is the heavy elemental materials. We considered the basic material was soda-lime glass and the heavy elemental materials included lead glass. (2) HAXPES brought out that the chemical states of Cs on particles, surface was different in the Na-poor areas and the Na-rich areas. In the Na-poor areas, the chemical state of Cs showed CsFeSiO mainly, but zero valence partly. In the Na-rich areas, the chemical state of Cs couldn't be identified. For above analyses, we can reveal the generation process of radioactive particles.
mainly, but zero valence partly. In the Na-rich areas, the chemical state of Cs couldn't be identified. For above analyses, we can reveal the generation process of radioactive particles.
Martin, P.*; Scott, T.*; Satou, Yukihiko
no journal, ,
Through the application of both laboratory and synchrotron radiation (SR) X-ray tomography (XRT), the internal structure of a representative 450  m
m  280
280  m
m  250
250  m particle was shown to be highly porous - with 24% of the internal volume constituted by void space. Compositional (elemental) analysis of the particulate material through SR X-ray fluorescence (XRF) detailed the peripheral enrichment of several elements (including Sr, Pb and Zr) - with the existence of Cs associated near-exclusively with the location of several highly-angular Fe-based fragments, extruding from the materials surface. Many larger fragments of cement composition were additionally observed embedded into the particles surface. SR X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) analysis on several high atomic density particles located within the bulk particle confirmed them to be U in composition, existing in the U(IV) oxidation state, as UO
m particle was shown to be highly porous - with 24% of the internal volume constituted by void space. Compositional (elemental) analysis of the particulate material through SR X-ray fluorescence (XRF) detailed the peripheral enrichment of several elements (including Sr, Pb and Zr) - with the existence of Cs associated near-exclusively with the location of several highly-angular Fe-based fragments, extruding from the materials surface. Many larger fragments of cement composition were additionally observed embedded into the particles surface. SR X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) analysis on several high atomic density particles located within the bulk particle confirmed them to be U in composition, existing in the U(IV) oxidation state, as UO . The isotopic analysis of this micron-scale U material enclosed just below the surface of the particle was subsequently determined using secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS), having spatially referenced their co-ordinate positions between the different techniques. SIMS mapping revealed the U-rich particle to be
. The isotopic analysis of this micron-scale U material enclosed just below the surface of the particle was subsequently determined using secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS), having spatially referenced their co-ordinate positions between the different techniques. SIMS mapping revealed the U-rich particle to be  1
1  m in maximum dimension, consisting of enriched U with 3.54 wt
m in maximum dimension, consisting of enriched U with 3.54 wt
 U - used in reactor Unit 1.
U - used in reactor Unit 1.
Kurosawa, Keiichi*; Iwata, Ayumu*; Satou, Yukihiko; Abe, Yoshinari*; Igarashi, Yasuhito*; Okuda, Tomoaki*
no journal, ,
The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident caused serious emission of radionuclides into the atmosphere. After several years, insoluble radiocaesium-bearing microparticles (CsMP) have been found in some regions in Japan. These insoluble solid particles remain as a particle in human airways and continue emitting radiation when they are inhaled. Therefore, these particles have a potentially significant adverse effect on human health. Because of the continuous emission of the  -rays, which is energetic electron beam, previous studies reported that the radioactive particles would have specific electrostatic charging characteristics. Also, several laboratory experiments and numerical simulations have shown that the electrostatically charged particles are more deposited on the human respiratory airway. Therefore, the electrostatic charging characterization of the CsMP is important for the accurate evaluation of its health effects. In this study, we used Kelvin Probe Force Microscopy to measure the surface potential of CsMP. The obtained mapping image was shown that the radioactive particle has a certain distribution of surface potential ranged between +0.3 V and -0.3 V. This distribution of the surface potential within the particle may be associated with the distribution of radioactive Cs in the surface layer of the particle.
-rays, which is energetic electron beam, previous studies reported that the radioactive particles would have specific electrostatic charging characteristics. Also, several laboratory experiments and numerical simulations have shown that the electrostatically charged particles are more deposited on the human respiratory airway. Therefore, the electrostatic charging characterization of the CsMP is important for the accurate evaluation of its health effects. In this study, we used Kelvin Probe Force Microscopy to measure the surface potential of CsMP. The obtained mapping image was shown that the radioactive particle has a certain distribution of surface potential ranged between +0.3 V and -0.3 V. This distribution of the surface potential within the particle may be associated with the distribution of radioactive Cs in the surface layer of the particle.
Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Koarai, Kazuma; Mitsuyasu, Yusuke*; Ono, Takumi*; Tamaki, Hiroaki*; Kino, Yasushi*; Sekine, Tsutomu*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; Chiba, Mirei*; et al.
no journal, ,
Release of the radioactive materials from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident results in a long-term low dose rate ionization exposure to wild animals. The biological effects of the wild animal do not show a clear correlation with the external dose, which is estimated from the external dose rate of the captured point of the animal, a precise external dose estimation using ESR and tooth enamel is required instead of using the external dose rate. In this work, we attempted to estimate the external dose of wild Japanese macaque and Procyon lotor captured in the high dose rate area.
Kusaka, Ryoji
no journal, ,
This presentation is the award-winning lecture of the Japan Society of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences 2019 Encouragement Award. It will be presented that the research achievements on the interface chemistry of lanthanide and actinide, which have been obtained by using vibrational sum frequency generation spectroscopy in the 4th research building of JAEA.
Sato, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
In order to clarify the properties of heavy actinide elements, we focused on the first ionization potential (IP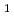 ), which is a physical quantity that directly reflects the binding energy of the outermost electron. To obtain information about the electron configuration of heavy actinide elements including element 103, lowrencium (Lr), the IP
), which is a physical quantity that directly reflects the binding energy of the outermost electron. To obtain information about the electron configuration of heavy actinide elements including element 103, lowrencium (Lr), the IP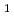 of fermium (Fm), mendelevium (Md), nobelium (No) and Lr were determined experimentally by using a novel method we have developed based on the surface ionization. From the results, it was clarified that No would have the quasi-closed shell structure [Rn]7s
of fermium (Fm), mendelevium (Md), nobelium (No) and Lr were determined experimentally by using a novel method we have developed based on the surface ionization. From the results, it was clarified that No would have the quasi-closed shell structure [Rn]7s 5f
5f and Lr would have one loosely-bound electron in the outermost electron orbital. We showed for the first time that the actinide series ends at Lr experimentally.
and Lr would have one loosely-bound electron in the outermost electron orbital. We showed for the first time that the actinide series ends at Lr experimentally.
 solution for understanding chemical species of Db
solution for understanding chemical species of DbAdachi, Sadia*; Sueki, Keisuke*; Toyoshima, Atsushi*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Komori, Yukiko*; Yokokita, Takuya*; Mori, Taiki*
no journal, ,
Anion exchange behavior of group-5 elements, Nb, Ta, and their pseudo homologue Pa in HF and HF/HNO solution was investigated to understand chemical properties of Db. Adsorption behavior of Db is clearly different from that of Ta and is similar to those of Nb and Pa. In the present study, anion exchange experiments of Nb, Ta and Pa were carried out with HF/HNO
solution was investigated to understand chemical properties of Db. Adsorption behavior of Db is clearly different from that of Ta and is similar to those of Nb and Pa. In the present study, anion exchange experiments of Nb, Ta and Pa were carried out with HF/HNO aqueous solution as basic experiments for estimating the species of Db fluoride complex. Adsorption behavior was investigated by changing the fluoride ion concentration for each HNO
aqueous solution as basic experiments for estimating the species of Db fluoride complex. Adsorption behavior was investigated by changing the fluoride ion concentration for each HNO concentration. Based on the observed distribution coefficients of these elements, we discuss the formation reaction of the anionic fluoride complex and chemical species of Db.
concentration. Based on the observed distribution coefficients of these elements, we discuss the formation reaction of the anionic fluoride complex and chemical species of Db.
 Cu using thermoseparation for cancer therapy
Cu using thermoseparation for cancer therapyOta, Akio*; Kawabata, Masako*; Motoishi, Shoji*; Saeki, Hideya*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Nagai, Yasuki*
no journal, ,
 Cu and
Cu and  Cu are recognized to be promising radioisotopes for cancer therapy and diagnosis in nuclear medicine. It is possible to produce both
Cu are recognized to be promising radioisotopes for cancer therapy and diagnosis in nuclear medicine. It is possible to produce both  Cu and
Cu and  Cu using accelerator neutrons from the zinc sample with different isotopic enrichment level, therefore the same separation procedure can be applied for both radioisotopes. Three-step-column separation chemistry was previously reported to separate
Cu using accelerator neutrons from the zinc sample with different isotopic enrichment level, therefore the same separation procedure can be applied for both radioisotopes. Three-step-column separation chemistry was previously reported to separate  Cu from the irradiated zinc sample. This paper reports that newly developed thermo-separation system to remove the bulk zinc from the sample using a difference in vapor pressure between Zn and Cu.
Cu from the irradiated zinc sample. This paper reports that newly developed thermo-separation system to remove the bulk zinc from the sample using a difference in vapor pressure between Zn and Cu.